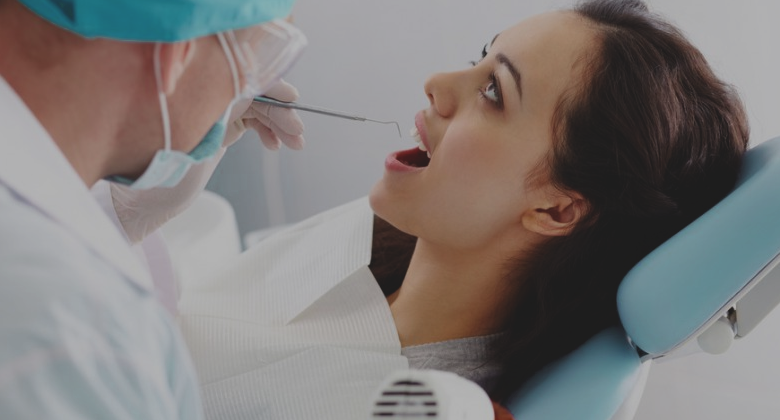
Aerobic Exercises
Aerobic and cardiovascular exercises develop endurance by engaging the body in repetitive workouts, such as running, swimming and hiking. According to Medline Plus, aerobic exercises are ideal for strengthening the heart and balancing cholesterol, due to the low-intensity, long-duration nature of the individual exercises. Adopt an aerobic exercise routine by adding a 30-minute power walk, jog or swim to your day. For best results, select an exercise that achieves your target heart rate for 20 to 60 minutes each day.
Strength Training Exercises
Although there are multiple approaches to strength training, from natural resistance training to isometric techniques, weightlifting is the most common method for building the strength and size of bodily muscles. For ultimate versatility, select two dumbbells of a challenging weight and develop a strength training workout routine that involves bicep, triceps, abdominal, pectoral, deltoid and trapezius muscle exercises. Select a body part and designate a day of the week for working out those specific muscle groups, for example: chest muscles on Monday, arm muscles on Tuesday. This allows your muscles sufficient time to rest between workouts. Also use your body weight in exercises like yoga to build strength in your arms, back, core, glutes and legs.
Flexibility Training And Yoga
Maintaining flexibility in your muscles, bones and ligaments is essential to preserving your mobility into old age. While most exercisers know to warm up with basic stretches, such as the hamstring and deltoid stretches, many individuals tend to neglect the importance of workouts devoted strictly to flexibility. When it comes to developing flexibility, few practices can compare with yoga; attend a yoga class at your local gym or fitness studio and learn the basic postures, such as the Sun Salutation sequence recommended by Yoga Journal.
Safety Requirements And Concerns
While most individuals can safely shift their activity level to meet the demands of these exercises, it is always recommended that you talk with your doctor or personal physician before embarking on a self-designated exercise regimen. Make sure you are physically fit enough to engage in any and all of the activities you plan to use to help reduce the risk of injury.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog


















