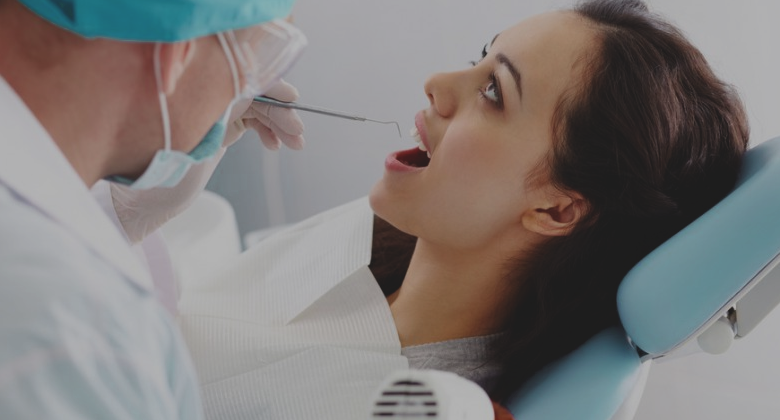
- From: Sunday 15 July 2018
- To: Saturday 15 September 2018
-
If you have any Dental Problem, KayaWell Expert Dr. Nitika Jain is providing free dental consultation for KayaWell users.
Every First Saturday of Month


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog










