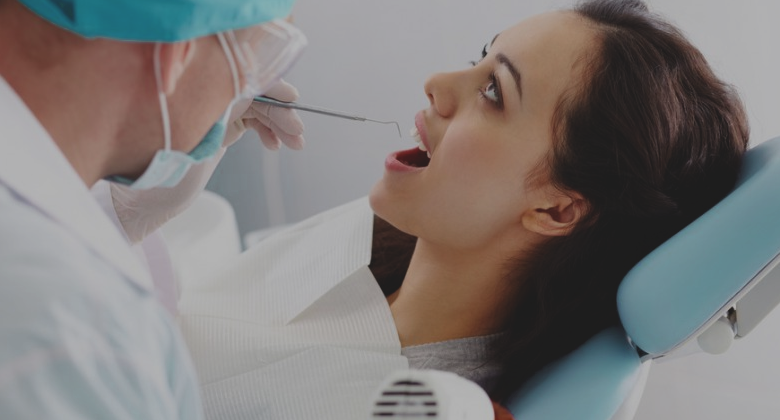
Classification of Yoga Asana
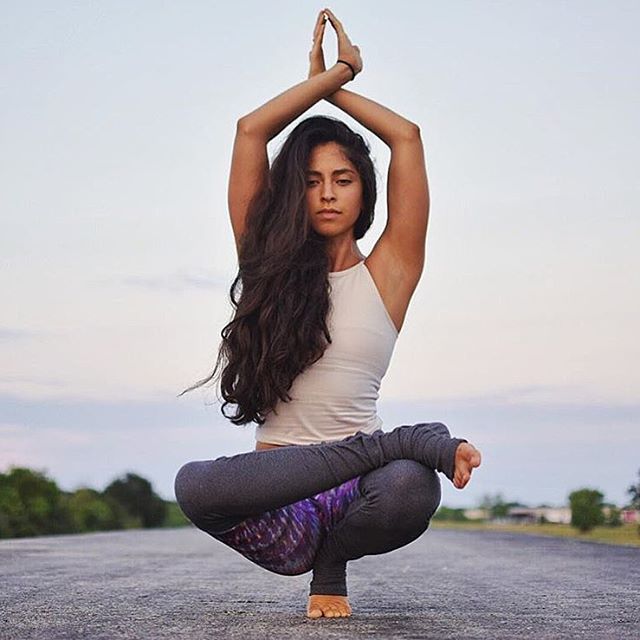
Advaita Yoga Ashrama categorizes yoga asana into three types, namely meditative, relaxing and cultural postures. Meditative postures, as the name suggest, are used for exercising meditation and pranayama. In the relaxing yoga asana, relaxation of mind is the foremost aspect. The practitioner holds meditative asana for a long span without getting distracted.
In the cultural yoga asana, muscles are worked upon. Some muscles relax, while some get stretched and some are contracted. The practice involves three groups, wherein two relax while one in a contract.
While practicing cultural posture, one must ascertain that muscles are stretched to the limit. During stretching, the practitioner should never experience the discomfort of any kind. Moreover, breath should always be kept under
Control.Sirsana,Sarvangasana,Matsyasana, Bhujangansana, Dhanurasana, Ardha Matsyendrasana, Pada Hastasana and Savasana are among most practised yoga asana.
Significance of Yoga Asana
The primary objective of practicing yoga asana is to render freedom from physical as well as mental discomfort. Yoga asana must provide comfort that rejuvenates body organs and helps in proper functioning of body mechanisms. An ideal asana should bring all the requisites of yoga into action, namely practice, breathing, and concentration.
Among benefits of practicing yoga asanas daily regimen is an improvement in flexibility, providing strength, reducing stress, reducing backache concerns, treating asthma, decreasing fatigue, lowering sleep disturbance and decreasing hypertension.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog


















