Defination
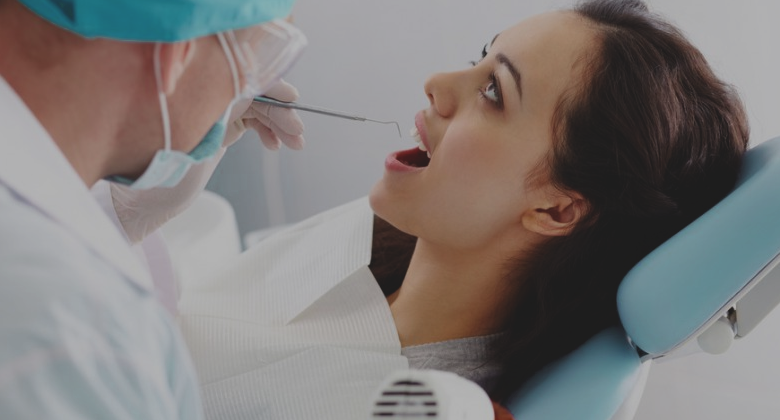
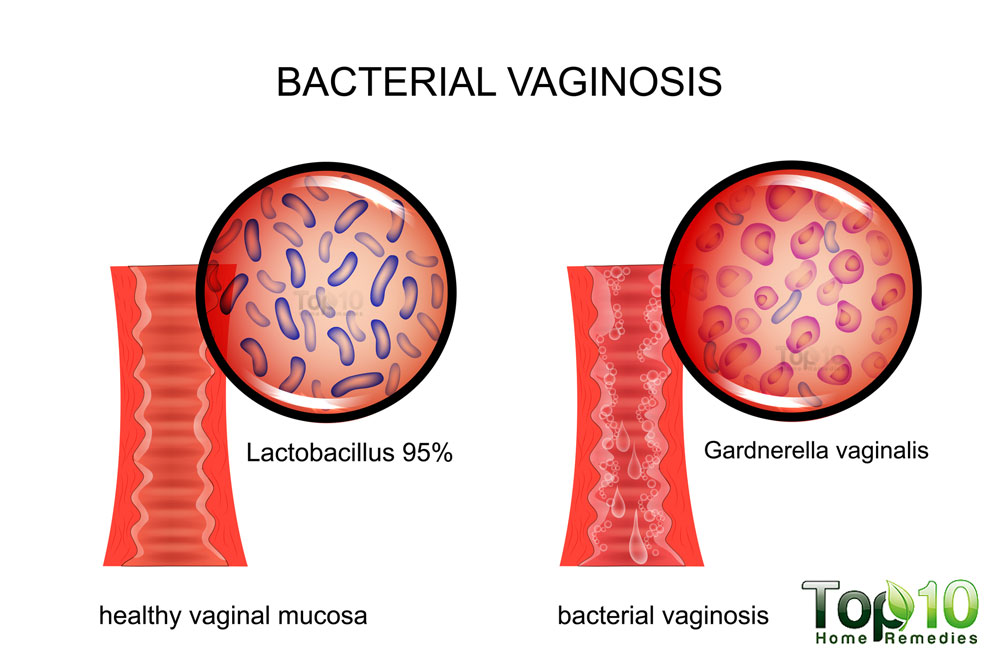
Bacterial vaginosis also is referred to as nonspecific vaginitis, is a vaginal condition that can produce vaginal discharge and results from an overgrowth of certain kinds of bacteria in the vagina. In the past, the condition was called Gardnerella vaginitis, after the bacteria that were thought to cause the condition. However, the newer name, bacterial vaginosis, reflects the fact that there are a number of species of bacteria that naturally live in the vaginal area and may grow to excess, rather than a true infection with foreign bacteria, such as occurs with many sexually-transmitted disease
Facts & Symptoms
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an abnormal vaginal condition that is characterized by vaginal discharge and results from an overgrowth of atypical bacteria in the vagina. It is not a true bacterial infection but rather an imbalance of the bacteria that are normally present in the vagina.
Bacterial vaginosis is not dangerous, but it can cause disturbing symptoms.
Most women do not experience symptoms of bacterial vaginosis, but when they do they are:
vaginal discharge, and
vaginal odor.
In diagnosing bacterial vaginosis, it is important to exclude other serious vaginal infections, such as the STDs gonorrhea and Chlamydia.
Treatment options for relief of bacterial vaginosis include prescription oral antibiotics and vaginal gels. Metronidazole (Flagyl) is one option for treating bacterial vaginosis.
Serious complications of bacterial vaginosis can occur during pregnancy, and recurrence is possible even after


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog
























Comments