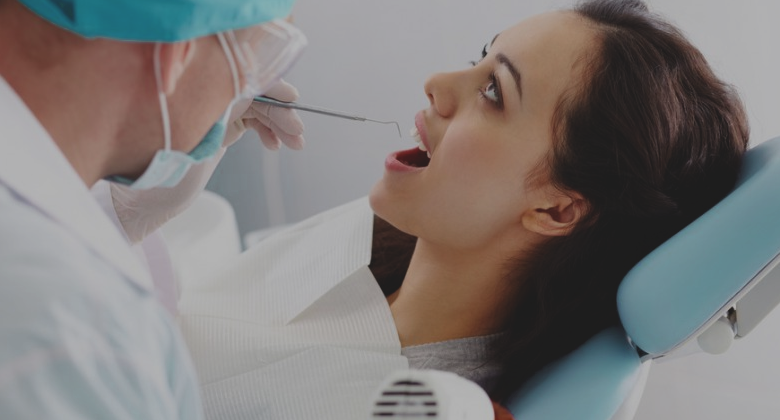
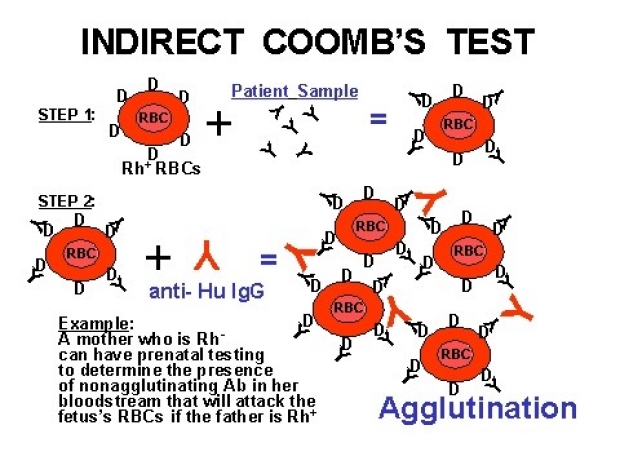
An indirect Coombs' test determines whether there are antibodies to the Rh factor in the mother’s blood.
A normal (negative) result means that the mother has not developed antibodies against the fetus's blood. A negative Coombs' test indicates that the fetus is not presently in danger from problems relating to Rh incompatibility.
An abnormal (positive) result means that the mother has developed antibodies to the fetal red blood cells and is sensitized. However, a positive Coombs' test only indicates that an Rh-positive fetus has a possibility of being harmed. A positive test cannot indicate the amount of fetal harm that has occurred or is likely to occur.
If test results show that antibody amounts are increasing during pregnancy, the fetus may be at greater risk of harm.
A fetus who is Rh-negative will not be harmed, even if the mother is sensitized.


 Contact Us
Contact Us




 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog
























Comments