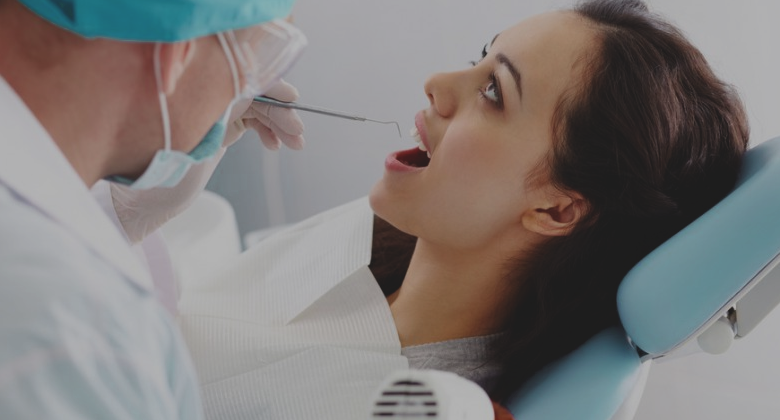
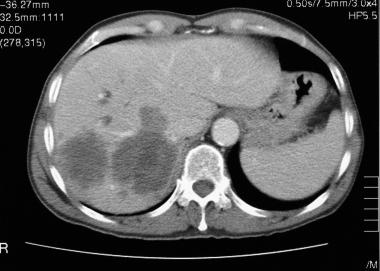
Triphasic spiral liver Computed Tomography (CT) is a standardized procedure for the detection and characterization of a large variety of benign and malignant liver lesions. This helps in the decline of mortality and morbidity rates among patients with liver disease. Spiral computed tomography has gained acceptance as the preferred computed tomography technique for routine liver evaluation because it provides image acquisition at peak enhancement of liver parenchyma during a single breath hold. In addition fast data acquisition allows successive scanning of the entire liver at different intervals after injection of the iodinated contrast material, thus creating the possibility of multiphase liver computed tomography.
Triphasic CT scan is a good non-invasive tool and can be used as first line imaging modality for differentiating benign and malignant focal liver lesions. Benign lesions like haemangioma can be reliably differentiated from malignant liver lesion; therefore unnecessary biopsies can be avoided. It is also particularly useful for hypervascular lesions which can be easily missed on routine CT scanning.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog
























Comments