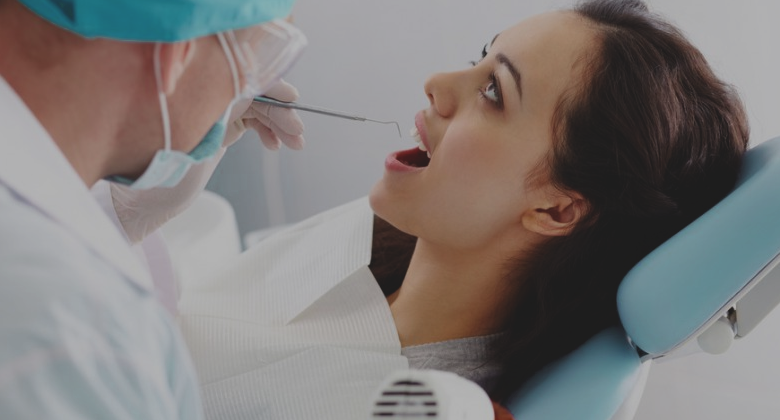
List of tests to diagnose erectile dysfunction
Common tests to diagnose the early stages of erectile dysfunction include:
Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
Some major treatment for erectile dysfunction:
1. Oral medications
People suffering from this condition are recommended erectile dysfunction medication like phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. It includes:
Sildenafil
Tadalafil
Vardenafil
Avanafil
These medicines improve blood flow to the penis. It facilitates erections along with sexual stimulation. You may see quick results if you are taking medicine for erectile dysfunction. Get in touch with a professional to avoid side effects.
2. Changes in your Lifestyle
One major reason for this condition is improper lifestyle. Therefore, making changes in your lifestyle is important as it positively impacts this condition. Some major steps include:
Quitting smoking offers numerous advantages. One significant health benefit of quitting smoking is the improvement in cardiovascular health, which reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke. Additionally, it enhances lung function, decreases the chances of developing cancer, and improves overall well-being.
Increasing physical activity has numerous advantages. Regular exercise can enhance cardiovascular health, boost mental well-being, and strengthen muscles and bones. Additionally, it helps in maintaining a healthy weight, improving sleep quality, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension.
These results in weight loss and managing chronic conditions such as hypertension and diabetes.
3. Psychological Counseling
These patients should attend therapy to treat the underlying stress and sadness. Relationship problems that may exacerbate ED can be resolved and performance anxiety can be addressed. Additionally, self-esteem can be raised with the aid of cognitive behavioral therapy and other psychotherapies.
4. Penile Injections and Suppositories
Supplements like MUSE or penile injections like alprostadil can be used for people who don't react well to oral drugs. With these therapies, an erection is induced, and blood flow is improved by injecting drugs directly into the penis or urethra. Many men find them beneficial, but they can have negative effects and need to be properly trained.
5. Vacuum Erection Devices
VEDs are used to create extra space around the penis, which draws them into it and causes an erection. After having an erection, a constriction ring is kept at the penis base to maintain the erection. It is an effective and non-invasive process that requires continuous practice for comfortable usage.
Conclusion
Erectile Dysfunction is commonly experienced by adults and older people. Do you feel dissatisfied with your sexual life? You must visit the doctor immediately. Common causes of this condition include diabetes and cardiovascular health. You may be involved in an open conversation with your healthcare expert to get proper treatment. Want to know how to treat ED? We have got you covered. The doctor will conduct a blood test to determine any underlying health condition. We hope this article helped you understand about erectile dysfunction in detail.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog

























Comments