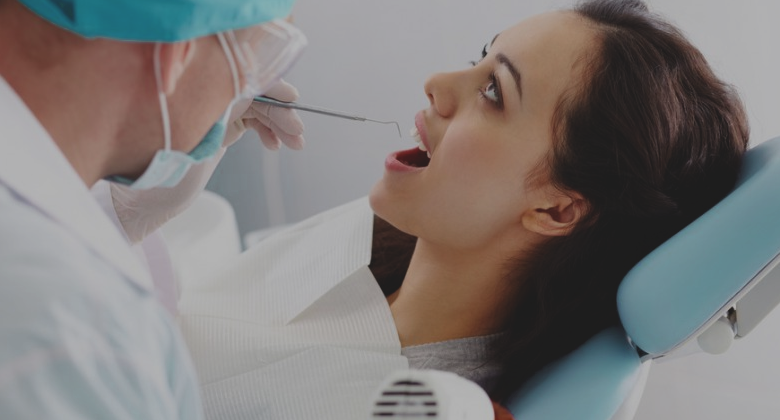
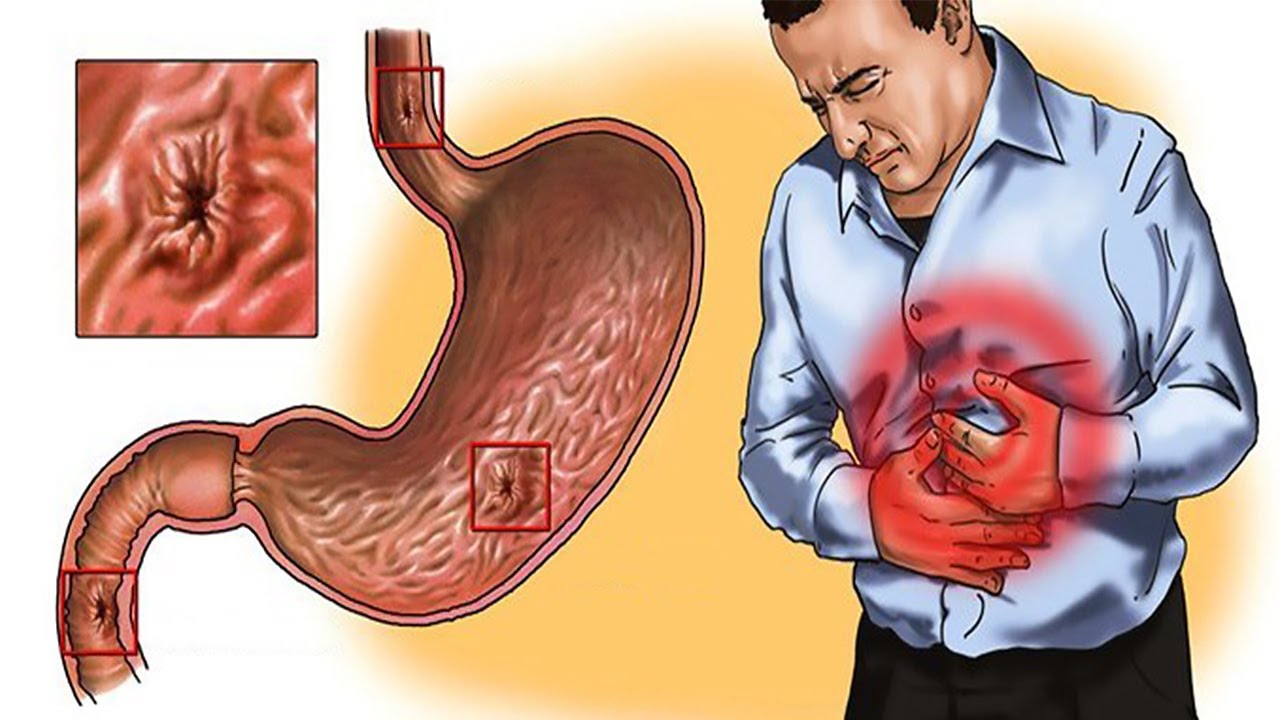
Treating the underlying cause of gastritis is the most effective way to reduce or resolve gastritis symptoms. For example, if the cause of gastritis is H. pylori, then treatment with appropriate antibiotics (usually a combination of amoxicillin and clarithromycin [Biaxin, Biaxin XL] plus bismuth subsalicylate [Pepto-Bismol]) should be effective to provide relief from symptoms.
If NSAIDs are the cause, then stopping the drug should be effective.
Other treatments often are used in addition to those that treat the specific cause of gastritis, many of which are over-the-counter or OTC, may reduce or stop symptoms of gastritis and allow gastric mucosal healing to begin regardless of the underlying cause. These medications include
. antacids (Maalox , Rolaids, and Alka-Seltzer),
. histamine (H2) blockers (famotidine [Pepcid AC], ranitidine [Zantac 75]), and
. PPI's or proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole [Prilosec], pantoprazole [Protonix], esomeprazole [Nexium]).
They all function by different mechanisms to reduce acid in the stomach but usually do not treat the underlying cause of gastritis.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog
























Comments