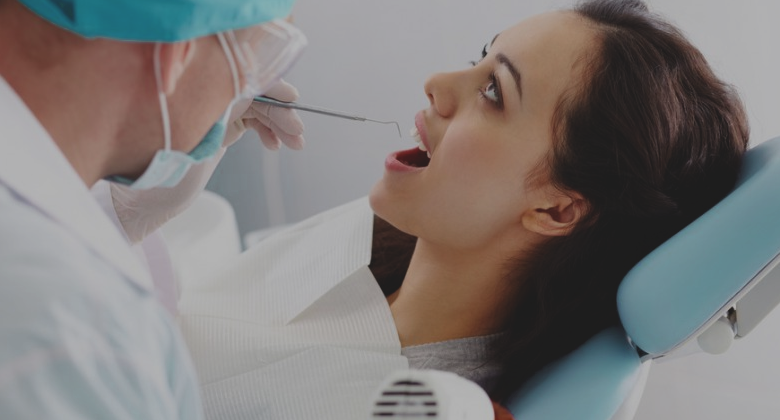
Occasional acid reflux is quite common, often occurring as a result of overeating, lying down after eating, or eating particular foods. The American College of Gastroenterology estimates that around 60 million Americans experience the heartburn of acid reflux at least once a month.
However, recurrent acid reflux, diagnosed as GERD, typically has other causes and risk factors and can have more serious complications.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease occurs in people of all ages, sometimes for unknown reasons (idiopathic).
In short, GERD occurs when the sphincter at the bottom of the esophagus becomes weak, or opens when it shouldn't.
GERD occurs more commonly in people who are:
. Overweight or obese - because of increased pressure on the abdomen.
. Pregnant - for the same reason as above.
. Taking certain medications - including some asthma medications, calcium channel blockers, antihistamines, sedatives, and antidepressants.
. Smoking - and exposure to second-hand smoke.
. Hiatal hernia is a condition where an opening in the diaphragm lets the top of the stomach move up into the chest; this lowers the pressure in the esophageal sphincter and raises the risk of GERD.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog

























Comments