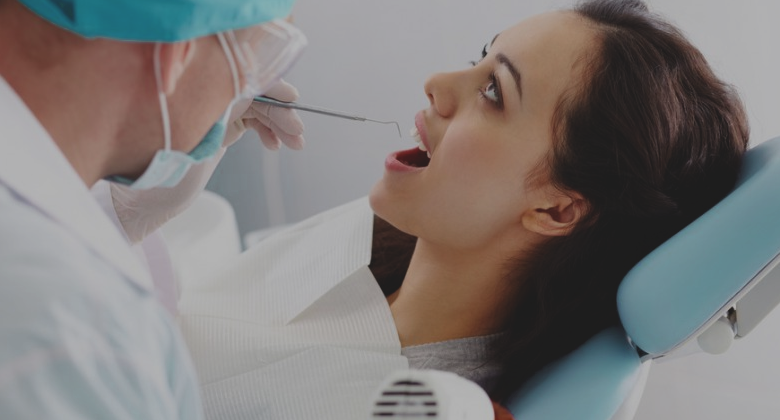
1. Natural Hormonal Changes
If you thought estrogen is an exclusive female hormone then you’re going to have to change that opinion because men are also capable of producing it, albeit in smaller quantities, just as testosterone is also produced by women, but in smaller quantities as well.
Men produce more testosterone which controls masculine traits like body and facial hair and muscle mass while women produce more estrogen that control feminine traits like breast growth.
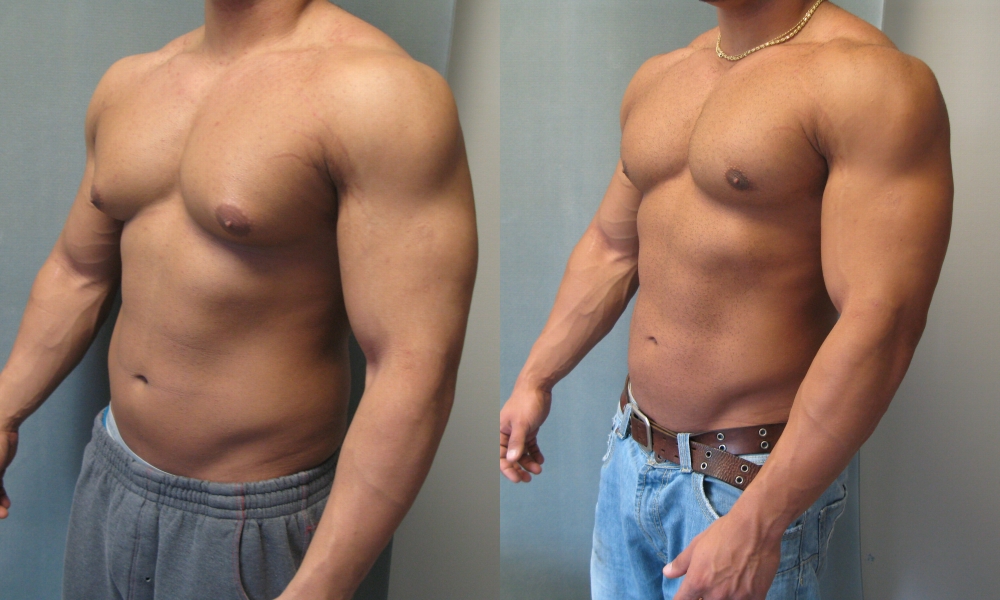
More estrogen than testosterone production causes gynecomastia.
2. Medications
Gynecomastia can be a side effects of using medications
This is where it got interesting. According to my doctor, between 10% and 25% of known cases of gynecomastia are attributed to the use of medications, resulting in gynecomastia which is non-physiologic.
3. Alcohol and Other Substances
Alcohol is also a trigger, along with methadone, amphetamines, heroin, and marijuana.
4. Chronic Diseases
Male individuals who have chronic diseases are also at risk for development of gynecomastia.
Kidney failure as a result of malnourishment in a male patient causes hormonal imbalances, my doctor said, because there is considerable damage in the testicles and suppressed testosterone production due to high urea levels, known as hypogonadism associated with uremia.
Hypogonadism causes significant diminished functionality of the gonads (testes in the case of males), which in turn interferes with the production of testosterone.
Pituitary insufficiency has been tightly connected with breast enlargement in men, as well as retardation of secondary sexual characteristics.
Among the most apparent symptoms of hypogonadism is small testicles.
Also, males who are afflicted with cirrhosis or liver failure are also susceptible to develop gynecomastic. If the liver is unable to metabolize estrogen, it is impaired.
Additionally, males who are alcoholics and already have liver disease are at high risk to acquire gynecomastia because the ethanol is liable to disrupt testosterone synthesis.
The phytoestrogens present in alcohol are also contributory to increasing the estrogen level higher than that of the testosterone.
5. Tumors
The presence of tumors – like Sertoli cell tumors or Leydig cell tumors – in the testicles could result in developing gynecomastia.
Other tumors which could alter the balance of the estrogen-testosterone ratio to cause or trigger male gynecomastia include pituitary gland tumors like prolactinoma, bronchogenic carcinoma, and adrenocortical tumors.
Male patients with prostate cancer condition may experience an onset of gynecomastia if treated with therapy using androgen deprivation.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog
























Comments