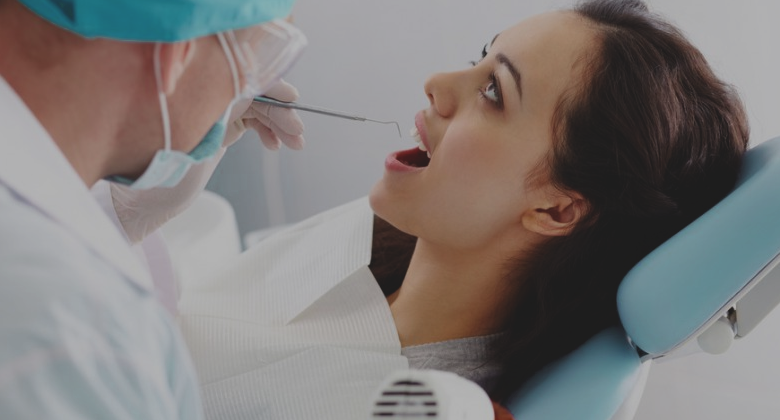
Nutrition and pregnancy refers to the nutrient intake, and dietary planning that is undertaken before, during and after pregnancy. Nutrition of the fetus begins at conception. For this reason, the nutrition of the mother is important from before conception (probably several months before) as well as throughout pregnancy and breast feeding. An ever-increasing number of studies have shown that the nutrition of the mother will have an effect on the child, up to and including the risk for cancer, cardiovascular disease, hypertension and diabetes throughout life.
An inadequate or excessive amount of some nutrients may cause malformations or medical problems in the fetus, and neurological disorders and handicaps are a risk that is run by mothers who are malnourished. 23.8% of babies worldwide are estimated to be born with lower than optimal weights at birth due to lack of proper nutrition. Personal habits such as smoking, alcohol, caffeine, using certain medications and street drugs can negatively and irreversibly affect the development of the baby, which happens in the early stages of pregnancy.
Caffeine is sometimes assumed to cause harm to the unborn baby but there is not enough evidence so say if this is true. A recent review showed that more research is needed to show whether caffeine intake effects birth weight, preterm births, gestational diabetes and other outcomes.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog

























Comments