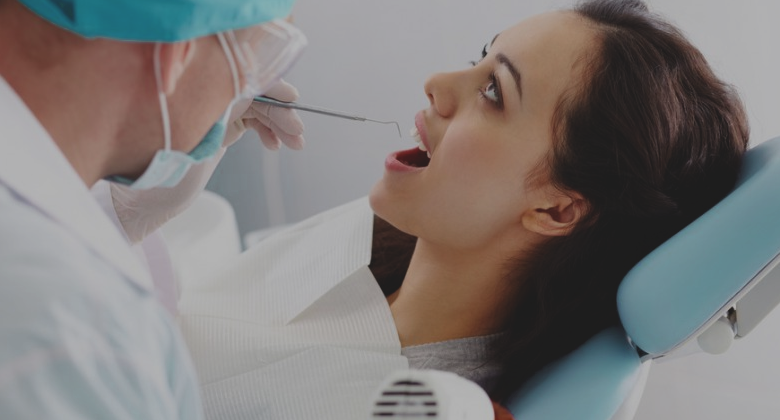
There are six basic types of nutrients that are considered essential to life: proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. These nutrients are needed for your body to function properly, and your diet is the source of them. Vitamins and minerals are considered micronutrients because they are needed in smaller quantities than the macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, and fat). Micronutrients do not provide calories. When your body does not absorb an adequate amount of any of the micronutrients, diseases can occur. It's important to understand what your nutritional needs are and how to achieve them.Vitamins are broken down into two categories: water-soluble and fat-soluble. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water. Leftover amounts are not stored and will leave your body through your urine. For this reason, you must consume them on a continuous basis. The water-soluble vitamins are the B vitamins and vitamin C. Fat-soluble vitamins dissolve in fat, not water. These vitamins need dietary fat in order to be better absorbed in the small intestines. They are then stored in the liver and fatty tissues (adipose tissues) and can accumulate to toxic levels when consumed in excess quantities. The fat-soluble vitamins are vitamins A, D, E, and K.Recommendations for essential nutrients are provided in the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) developed by the Institute of Medicine of the National Academies. Dietary Reference Intakes is the general term for a set of reference values used for planning and assessing nutrient intake for healthy people. There are three important types of DRI reference values; Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA), Adequate Intakes (AI), and Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (UL). The RDA is set to meet the nutrient requirements for the average daily intake of nearly all healthy individuals in each age and gender group. When there is insufficient data to set an RDA for a nutrient, an AI is set. AIs meet or exceed the amount needed to maintain an adequate nutritional state in nearly everyone of a specific age and gender group. Some nutrients can cause health problems when consumed in excessive quantities. The UL was set to provide the maximum daily intake that is unlikely to result in adverse health effects. Numerous health conditions, however, can impact your nutritional needs. A registered dietitian or physician can help you better determine your needs based upon your overall health and condition.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog

























Comments