What are the obvious signs and symptoms for Vitamin D deficiency?
Adults who are deficient in Vitamin D may have the following signs and symptoms:
fatigue, aches and pains
Stress fractures, which are most common in the legs, pelvis, and hips, cause severe bone or muscle pain and weakness.
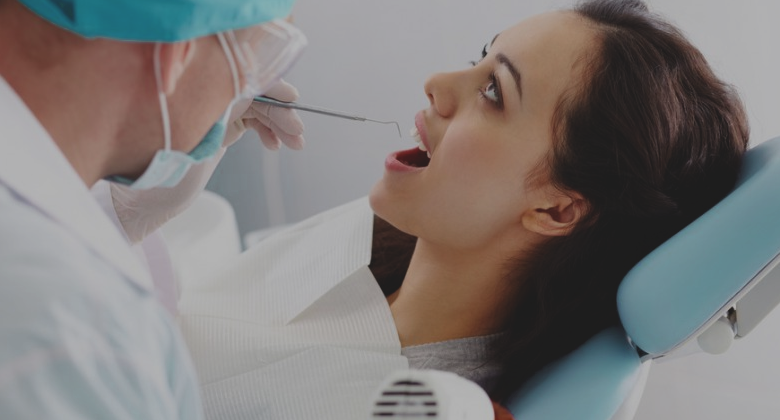
A healthcare professional can detect Vitamin D deficiency with a simple blood test. If you have a deficiency, your doctor may do X-rays to check the strength of your bones.
If you have a Vitamin D deficiency, your doctor will probably recommend that you take Vitamin D supplements. If you have a severe deficiency, they may offer high-dose Vitamin D tablets or liquids instead. You should also make sure you get adequate Vitamin D from sunlight.
Indeed, even while the body can produce Vitamin D, an inadequacy can happen for an assortment of reasons.
Causes:
Vitamin D supplementation is required for infants who are solely breastfed, especially if their skin is dark or they have minimal sun exposure. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, all breastfeeding newborns should take 400 international units (IU) of oral Vitamin D every day.
The Health Benefits of Vitamin D

Bones in decent condition:
Here’s the answer to your question, what is Vitamin D good for? Vitamin D is quite essential for calcium and the support of phosphorus levels in the blood Trusted Source. Minerals are required for bone health. Vitamin D is needed to activate and absorb calcium in the intestines, as well as to reclaim calcium that would otherwise be expelled by the kidneys. Vitamin D deficiency in children can cause rickets, a condition in which the bones deteriorate and the child appears badly bowlegged.
Vitamin D deficiency in adults produces osteomalacia, or bone weakening. Muscle weakness and inadequate bone density are symptoms of osteomalacia. Osteoporosis, which affects over 53 million individuals in the United States and puts them at danger, can be caused by a Vitamin D shortage.
Vitamin D has been demonstrated to lift one's spirits and reduce depression
In research, Vitamin D has been shown to play a role in mood modulation and lowering the risk of depression. In a study of 7,534 adults, those who took Vitamin D supplements and had negative feelings found that their symptoms improved. Vitamin D supplementation may help those who are depressed and have a Vitamin D deficiency.
In another study, low Vitamin D levels were connected to more severe fibromyalgia symptoms, anxiety and depression. A Vitamin D deficiency can induce osteoporosis, which affects about 53 million people in the United States and puts them at risk.
Vitamin D may aid in illness prevention.
Vitamin D has been related to the following, in addition to its primary effects:
Prevention of multiple sclerosis- According to a 2018 review of population-based studies, low Vitamin D levels are linked to an increased risk of MS.
Heart disease risk is reduced-Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to a higher risk of heart disease, such as hypertension, heart failure, and stroke. However, it is unclear if Vitamin D insufficiency causes heart disease or simply indicates poor health in those with chronic illnesses.
Reducing the likelihood of major illness- According to various studies, Vitamin D may help prevent severe flu and COVID-19 infections. According to a new study, Vitamin D insufficiency has been related to acute respiratory distress syndrome.
The immune system is bolstered-People who don't receive enough Vitamin D are more likely to have infections and autoimmune conditions such rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and inflammatory bowel disease.
It has the ability to help you shed pounds:
Low Vitamin D levels are more common in obese adults.
According to one study, obese persons who took Vitamin D supplements along with a weight-loss diet plan lost more weight and fat mass than those who merely followed the diet plan.
People who received calcium and Vitamin D supplements lost more weight than those who took a placebo supplement in a previous trial. The extra calcium and Vitamin D, according to the researchers, may have decreased hunger.
Despite the lack of proof that Vitamin D induces weight reduction, there does appear to be a link between Vitamin D and weight loss.
Vitamin D can aid in the control of blood sugar levels.
Vitamin D is required for the metabolism of glucose found in diet. It also induces the beta cells in your pancreas to produce insulin, a hormone that is necessary for converting food into energy and controlling blood sugar, according to Dr. Shapses. It also lowers insulin resistance (when your body doesn't respond as effectively to insulin) and may help prevent type 2 diabetes, according to the ODS.
While there is "limited evidence" of a cause-and-effect relationship between low Vitamin D levels and higher blood sugar levels (in both those with and without diabetes) as well as an increased risk of diabetes, several observational studies have found a link between low Vitamin D levels and an increased risk of diabetes.
Overdoing it on Vitamin D has its drawbacks:
You could receive too much Vitamin D if you use a lot of Vitamin D supplements. In any case, in light of the fact that your body manages the amount of Vitamin D created by sun openness, this is probably not going to happen through food or sun openness.
A lack of Vitamin D can cause blood calcium levels to rise. A number of health problems may result, including nausea, apathy, vomiting, confusion, increased thirst, and abdominal pain
And dehydration.
Food Sources of Vitamin D
Here is the answer to the question; what foods have Vitamin D? Only a few foods contain Vitamin D3. The best sources are fatty fish meat and fish liver oils. Smaller levels can be found in egg yolks, cheese, and beef liver. Vitamin D2 is found in some mushrooms, and some commercially available mushrooms have higher levels of D2 due to intentional exposure to high levels of ultraviolet radiation. Vitamin D is found in a wide range of foods and supplements, including dairy and cereal. Here are some of the Vitamin D rich foods:
1. Mushrooms, A Vitamin D-rich meal
Mushrooms are a rich source of Vitamin D. Because of its high Vitamin D content, it should be included in your diet at least four times per week. It's one of the most Vitamin D-rich foods, and it'll help you get more of it. It's completely up to you how you prepare it; you may cook, bake, or pan-fry it for a tasty and nutritious snack. Sun Drying mushrooms before eating them is thought to boost their nutritional worth because they emit Vitamin D naturally when exposed to sunlight.
2. Cheese
Do you need another reason to adore and savor cheese? Cheese is one of the most Vitamin D foods. The simplest and most delicious method to solve your Vitamin D deficiency is to eat more cheese. Of all the cheeses, ricotta has the highest Vitamin D content. Adding a second layer of cheese to your morning toast may not be such a bad idea after all.
3. Fish
All types of fish, including mackerel, tuna, trout, and eels, are high in Vitamin D. More oily or fatty fish, such as thick filets of salmon, have more Vitamin D than less oily fish.
4. Egg
In eggs, you'll find a lot of Vitamin D. The vitamin is found in the yolk of an egg. As a result, for a balanced vitamin intake, it's vital to use the entire egg, not just the whites. When eating eggs, always remember to eat the most nutritional part of the egg, the yolk. Keep in mind, however, that it is one of the foods high in Vitamin D. According to the claims, eating one egg a day will provide you with 10% of your daily vitamin requirement.
5. Soy-Milk
So, what is soy-milk, exactly? To make this plant-based milk, soybeans are soaked, dried, and ground in water. Soymilk is high in Vitamin D, as well as other vitamins such as Vitamin C and iron, and contains about the same amount of protein as regular cow's milk.
What Vitamin D Won't Do for Your Well-Being?
Scientists are still attempting to find out how Vitamin D affects our bodies and what role it might play in illness prevention and treatment, as you're probably aware. But one thing is certain: Vitamin D isn't a miracle cure, so don't start popping tablets in the hopes of curing everything.
That is something that no vitamin can accomplish.
What You Should Know About Vitamin D and Your Health:
Vitamin D is an important nutrient that can help strengthen bones and keep them healthy, as well as potentially lowering cancer risk and death in some people. However, further research into the vitamin's various effects is needed before scientists, doctors, and the general public can make informed decisions about supplementing or increasing dietary intake.
Until then, make sure you're getting enough Vitamin D through your food, supplements, and exposure to the sun. If you suspect you may be lacking in Vitamin D, talk to your doctor about getting a blood test to see if your levels are within acceptable limits.
Summary:
Vitamin D aids in the digestion of calcium and phosphate in the diet. In terms of efficiency, D3 trumps D2. Food, supplements, and sun exposure are all sources of Vitamin D.
Vitamin D is necessary for the health of bones and muscles, as well as the immune system. It has the potential to help with depression treatment, inflammatory disease treatment, and cardiovascular disease prevention.
Every day, adults under the age of 70 should ingest 600 IU. Adults over 60 years old should take 800 IU. Taking Vitamin D tablets is the most reliable way to ensure optimum Vitamin D levels.
If you take too much, toxic repercussions can ensue.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog


















Comments