What is Trachoma?
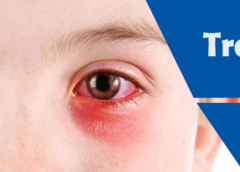
Trachoma is a Chlamydia trachomatis infection of the eyes, which is the leading cause of preventable blindness. While being very strong in developed nations, it is abundant in overcrowded regions with restricted access to clean water and healthcare.
It’s characterized by eye discharge and repeated infections tend to curl the eyelashes into the eye. This can lead to corneal scratching, blurred vision, and ultimately vision loss. Below are discussing the Trachoma and its Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors and Prevention tips.
What are the symptoms of trachoma?
The most common signs that a person is suffering from trachoma include:
Since the infection spreads by hands, clothing, and bedding, it affects women and children disproportionately: women globally are almost two (1.8) times more likely to be blinded by the disease than men. This can lead to trichiasis if trachoma is not treated.
When to seek medical attention
When they feel some pain or discharge from their child’s eye, you should call the doctor particularly if they have recently travelled to places where trachoma is common.
What is the cause of trachoma?
Infection with the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis causes trachoma.
The condition happens all over the world. It’s most commonly seen in a developing country in rural areas. Children frequently get affected. The scarring caused by the infection can however not be detected until later in life. The disease is rare in the United States. And in crowded or unclean living environments it is more likely to occur.
Trachoma is spread by direct contact with fluids in the infected eye, nose, or throat. Contact with contaminated objects, such as towels or clothing, may also pass it on. Some flies will spread the bacteria, too.
Risk factors of trachoma
Trachoma is associated with poor personal and community hygiene and is often linked to poverty.
Specific risk factors include:
What are the Complications of Trachoma Infection?
A single trachoma infection is easily treated with antibiotics. Repeated and recurrent infections, which are bound to occur in highly endemic areas, can result in long-term complications such as:
Prevention
If you have received antibiotics or surgical treatment for trachoma, reinfection is always a concern. For your protection and others’ safety, be sure that family members or others with whom you live are screened and treated for trachoma, if necessary.
Trachoma may occur globally but is more common in the Middle East, North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, and South Asia and China. Take special care while doing good hygiene in regions where trachoma is widespread, which can help prevent infection.
Proper hygiene practices include:
- Wash your face and wash your hands. Maintaining faces clean may help break the reinfection cycle.
- Flies Control. Reducing the fly populations may help eradicate a significant transmission source.
- Handling waste properly. Animal and human waste properly disposed of will every breeding ground for flies.
- Improved water access. Having a nearby source of freshwater will help improve the hygienic conditions.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.