RINGWORM OVERVIEW
Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm. Ringworm is actually an infection caused by a fungus. It is called ringworm because it can cause a ring-shaped, red, itchy rash on the skin. Ringworm is also called tinea.
There are several different types of ringworm infections, which are named from the body-part that is affected:
●Tinea capitis affects the top of the head, or scalp, and is found mostly in children
●Tinea pedis affects the feet, and is also called "athlete's foot"
●Tinea cruris affects the groin, and is also called "jock itch"
●Tinea faciei affects the face
●Tinea barbae affects the beard area
●Tinea manuum affects the hands
●Tinea corporis is the catch-all term for tinea infections on other body surfaces
You can catch ringworm from someone else who is infected, or even from an infected dog or cat. You can also catch it from objects, such as a shower stall, locker room floor, or pool area that has the fungus. Plus, you can spread ringworm from one body part (such as your feet) to another (such as your groin or hand).
If you have ringworm, your healthcare provider may be able to diagnose it just by looking at your rash. In some cases, s/he will take some scrapings of the rash and look at it under a microscope to check for the fungus. Rarely, a healthcare provider may need to send scrapings from the rash for a fungal culture (a test used to identify fungus by growing it in a microbiology laboratory).
This article will discuss the symptoms and treatment of each type of ringworm infection. More detailed information about tinea is available by subscription Fungal nail infections are also discussed separately.
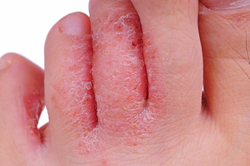
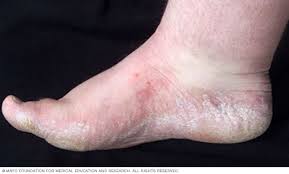
ATHLETE'S FOOT (TINEA PEDIS)
Tinea pedis causes the skin on the feet – often between the toes – to become itchy, red, cracked, tender, and scaly . Sometimes it also causes blisters to form. People who have tinea pedis often also have the infection on the palms of their hands, in their nails, or on their groin.
Unlike tinea capitis, tinea pedis responds to most topical antifungal treatments, many of which are available without a prescription. The cream/gel/lotion/powder is usually applied once or twice daily for four weeks . In severe or long-lasting cases, your healthcare provider may suggest an oral antifungal drug (which is available only by prescription).
To improve comfort and reduce the chances of repeat infection, it is a good idea to use antifungal foot powders, both on the feet and in the shoes, and to wear open shoes when feasible, at least while the feet heal.


 Contact Us
Contact Us



 Hospitals
Hospitals
 Doctors
Doctors
 Diagnostic
Diagnostic
 Pharmacy
Pharmacy
 Health Tips
Health Tips
 Blog
Blog